
You may wonder how moisture tissue paper stays strong when wet. This special paper uses smart materials and a good design. People use it every day in kitchens, bathrooms, and at work. Its strength helps you clean up spills or wrap food. It can handle hard jobs without breaking. Think about the science used to make something so simple and useful.
Key Takeaways
Wet strength tissue paper does not break when wet. This makes it good for cleaning, crafts, and food wrapping. The mix of cellulose fibers and wet strength resins makes the paper strong and able to soak up water. Pick wet strength tissue paper for art so your work stays bright and does not fall apart. Try to find eco-friendly choices that are strong and safe for nature. Test many brands of paper towels to see which one soaks up the most water for you.
Wet Strength Tissue Paper
What Makes It Different
Wet strength tissue paper is not like regular tissue paper. When you use it, it does not break when wet. This paper stays strong during painting or gluing. You can use it for crafts, cleaning, or wrapping food. The fibers and resins inside make it tough. It feels light but does not fall apart easily. If you want to dye, paint, or print, it holds color well. You see bright colors that make your projects stand out. Acid-free tissue paper keeps your work looking good and stops yellowing.
Here is a quick comparison:
| Feature | Wet Strength Tissue Paper | Conventional Tissue Paper |
| Strength when wet | Stays strong and does not break | Breaks easily when wet |
| Durability | Good for crafts and projects | Thin and easy to tear |
| Suitability for projects | Works well with water, glue, or paint | Not good for wet projects |
| Color retention | Keeps color bright and clear | Color may fade when wet |
| Acid-free | Helps art last longer | May not be acid-free |
Tip: Pick wet strength tissue paper for projects that need to last and look bright.
Why Integrity Matters
You use wet strength tissue paper for many things. When you clean spills, you want the paper to stay together. In art, you need it to hold paint and glue. In factories, workers use it because it keeps its shape and cuts down on waste. You get better results and save time.
Here is why integrity matters:
Usability: You use it without worrying about rips.
Durability: It stays together even when wet.
Operational Efficiency: Workers see less waste and smoother work.
Wet strength tissue paper helps you feel sure. You know it will work well at home or at work.

Moisture Tissue Paper Materials
Cellulose Fibers
Cellulose fibers are the main part of wet strength tissue paper. These fibers come from plants, mostly trees. When you look at the paper, it looks soft and fluffy. The fibers give the paper its strength and softness. They also help the paper soak up water.
Here is a table that shows what cellulose fibers do for the paper:
| Property | Description |
| Strength | Makes the paper tough and hard to tear or stretch, even when wet. |
| Softness | Gives the paper a fluffy feel, making it nice for cleaning. |
| Absorbency | Lets air and water move in, so the paper soaks up moisture well. |
Some tissue paper feels stronger or softer than others. This depends on where the fibers come from. Softwood fibers are long and rough. They make the paper strong and help it stay together when wet. Hardwood fibers are short and smooth. They make the paper soft and gentle on your skin. Mixing both types gives you a good balance. The paper feels soft but does not break easily. Birch kraft pulp is one example. It makes the paper strong, absorbent, and soft.
Cellulose helps the paper soak up water. The fibers have tiny spaces between them. Water goes into these spaces and spreads out. This helps the paper pick up spills fast. You see this when you use a paper towel to clean up.
Note: Using the right mix of fibers gives you both comfort and strength in wet strength tissue paper.
Wet Strength Resins
Fibers alone cannot make wet strength tissue paper stay strong when wet. Wet strength resins are also needed. These chemicals help the fibers stick together, even with water. Without resins, the paper would fall apart when wet.
Manufacturers use different wet strength resins. The most common ones are:
Urea/formaldehyde resins
Melamine/formaldehyde resins
Polyamide-amine-epichlorohydrin (PAE) resins
These resins work deep inside the paper. For example, PAE resin has cationic azetidinium groups. These groups stick to the negative spots on cellulose fibers. The resin then makes strong chemical bonds between the fibers. This cross-linking helps the paper resist water and stay strong.
Here is a table that shows how some resins work:
| Wet Strength Resin | Function at Molecular Level |
| PAE Resin | Has cationic azetidinium groups that stick to anionic spots on fibers, making the paper strong when wet by cross-linking. |
| FennoStrength™ | Works as a wet strength agent, but details are not given. |
| METRIX™ | Works as a wet strength agent, but details are not given. |
Wet strength agents act like glue for the fibers. They cross-link the cellulose, making the bonds stronger. This gives the paper its water absorption and toughness.
Wet strength agents glue cellulose fibers together.
These chemical bonds help the paper resist water.
The tissue stays strong and soaks up water well.
But there are some things to watch out for. Making wet strength resins can create harmful by-products. Chemicals like DCP and MCPD may form during production. These can be bad for your health. They may cause cancer or genetic problems. Because of this, there are rules to limit these chemicals in products that touch food.
Tip: Always check if your moisture tissue paper is safe for food use, especially if you use it for wrapping or serving.
How Do Paper Towels Absorb Water
Capillary Action
When you clean a spill with a paper towel, water moves into the towel fast. This happens because of capillary action. Capillary action means water travels through tiny spaces in the towel. The fibers make these small gaps. Water sticks to the fibers because of adhesive forces. Water molecules also pull on each other with cohesive forces. These two forces help water move up, even against gravity.
Water goes into small spaces between fibers because of adhesive forces.
Cohesive forces between water molecules pull more water into the towel.
If you dip a paper towel in water, you see the liquid climb up through tiny pores.
This explains why paper towels soak up water so well. The science of absorbency shows that the towel’s structure and the fibers matter. Cellulose fibers have lots of hydroxyl (OH) groups. These groups make hydrogen bonds with water molecules. This helps the towel grab and hold water.
Did you know? Water moves through a paper towel like plants pull water from their roots.
You can try this at home. Dip the edge of a paper towel in colored water. You will see the color move up the towel. This shows capillary action.
Fiber Bonding
Moisture tissue paper is strong and absorbs water because of how the fibers stick together. The type of fiber and how they connect are important. Pulping, refining, and pressing change how much water paper towels can soak up.
| Process Type | Impact on Absorbency and Strength |
| Pulping methods | The right method helps the towel hold more water. |
| Mechanical refining | Makes fibers bigger and helps them swell, so the towel absorbs more. |
| Pressing techniques | Changes how fibers stick and how the sheet forms, which affects water absorption. |
| Lamination and embossing | Helps the towel soak up water without making it weak. |
Manufacturers use special ways to help fibers bond well. Wet strength resins keep the paper web strong when wet. Mechanical refining makes fibers more flexible and helps them bond better. Chemical changes, like adding poly(vinyl alcohol), make a network that holds water and keeps the towel strong. Hydroxyl groups in cellulose and poly(vinyl alcohol) help make strong bonds.
Wet strength resins make the paper web stronger.
Debonding agents can make natural fiber bonds weaker, but wet strength resins fix this.
Chemical changes with poly(vinyl alcohol) help fibers bond better.
Poly(vinyl alcohol) makes cross-linked networks that help absorb water and bond fibers.
Hydroxyl groups in poly(vinyl alcohol) help it stick to cellulose.
Different brands of towels soak up different amounts of water. You should test how much water each towel can hold. Try each brand a few times and mix up the order for fair results. This helps you find the best towel for your needs.
Tip: For a towel that absorbs more water, pick one with strong fiber bonding and a good sheet design.

Manufacturing and Design
Fiber Selection
Wet strength tissue paper is made with special fibers. Manufacturers pick fibers that help the paper stay strong when wet. They often mix softwood and eucalyptus fibers. Softwood fibers make the paper strong. Eucalyptus fibers make it soft. You want paper that feels good and does not fall apart when wet.
Manufacturers treat the fibers to make them better. They check if the paper keeps its strength after getting wet. The paper should keep more than 15% of its dry strength. This way, you get paper that is both comfy and tough.
| Criteria | Description |
| Fiber Type | Softwood for strength, eucalyptus for softness |
| Treatment Processes | Special treatments improve wet and dry strength |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Choosing affordable fibers keeps production costs down |
| Strength Properties | High wet and dry strength with less fiber material |
Resin Application
Good fibers are not enough for wet strength tissue paper. Wet strength resins are very important. These resins make strong bonds with cellulose fibers. The bonds do not break when the paper gets wet. Heat is used to cure the paper. This makes the paper firm and hard to tear.
Wet strength resins link fibers with strong bonds.
Cationic resins help the paper stay strong when wet.
The right resin makes the paper better and tougher.
| Aspect | Impact on Tissue Paper |
| Wet Strength | Increases wet tensile strength |
| Production Cost | High resin use can raise costs |
| Quality | Better resin means better performance |
Tip: New resins use more renewable materials. This helps the planet and keeps the paper strong.
Sheet Formation
Sheet formation mixes fibers and resins to make a smooth sheet. The fibers and fillers must spread out evenly. Good sheet formation means no weak spots in the paper. Bad formation causes thin or thick areas that tear easily. Even sheets make the paper last longer and stay strong.
Even fiber spread makes the paper strong and tough.
Curing locks in the strong bonds during sheet formation.
The finished paper dries firm and does not tear when wet.
When you use moisture tissue paper, you get a strong product. Careful steps in making it help you trust it for hard jobs.
Applications
Food Packaging
Moisture tissue paper is used in lots of food packaging. This paper stays together even when wet. You see it in wraps for frozen food and seafood trays. It is also in takeout boxes and liners that stop grease. These uses help keep food fresh and safe. The paper soaks up water to stop leaks. It keeps food looking nice. You do not need to worry about the package tearing or getting soggy.
Wet strength matters a lot here. It lets you handle food safely. The packaging stays strong in humid places. Many companies pick this paper because it meets high standards. You can compare how strong different tissue papers are:
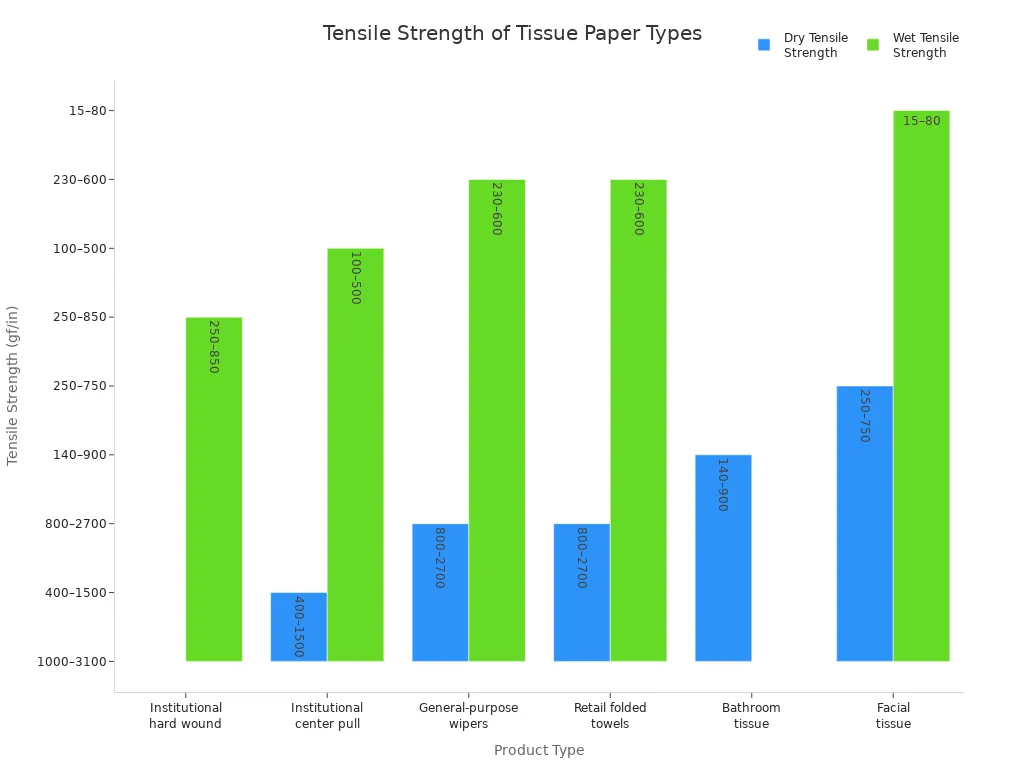
| Product | Dry Tensile Strength (gf/in) | Wet Tensile Strength (gf/in) |
| Institutional paper towels – hard wound | 1000 – 3100 | 250 – 850 |
| Institutional paper towels – center pull | 400 – 1500 | 100 – 500 |
| General-purpose wipers | 800 – 2700 | 230 – 600 |
| Retail paper towels – folded | 800 – 2700 | 230 – 600 |
Art and Crafts
Wet strength tissue paper is great for creative projects. This paper does not break when wet. You can use it for lanterns, willow crafts, and models. It soaks up water, so you can paint or glue without ripping it. Artists like it for collage and Gelli printing. It lets them make detailed designs and layers. The paper is light and acid-free, so your art lasts longer.
Stays strong for flexible and tough projects
Good for wrapping, layering, and reinforcing
Helps prints stay bright and last long
Tip: Pick this paper for art that needs to look good and last.
Industrial Uses
Industries use moisture tissue paper for cleaning and packaging. It can replace cloth or plastic because it is strong and useful. The paper soaks up water and handles spills well. It does not fall apart when wet. You see it in beverage cases, lawn bags, and hygiene products.
| Industrial Use | Performance Requirement |
| Replacement for cloth (paper towels) | Must stay strong when wet |
| Replacement for plastic (lawn bags) | Needs wet tear strength |
| Replacement for coolers (beverage cases) | Should keep most dry strength when wet |
Wet strength is very important in these jobs. It helps the paper resist water and keep its shape. This means you get good results, even for hard tasks.
Note: Many companies now want eco-friendly products. They look for options that are better for the environment and follow new rules.
You have learned how moisture tissue paper stays strong when wet. Synthetic adhesives, chemical cross-linking, and ether bonds help it last a long time:
| Principle | Effect |
| Synthetic adhesives | Make covalent bonds for wet strength |
| Cross-linking cellulose | Makes the paper stronger when wet |
| Ether bonds | Fight water, so the paper stays together |
Manufacturers pick good pulp, add special resins, and use smart steps to make each sheet strong and dependable. You get products that work well for art, food packaging, and cleaning. Companies keep making these papers better for the planet and for you. When you use a tissue next time, think about the science that makes it work!
FAQ
What gives moisture tissue paper its strength when wet?
You get strength from a mix of special fibers and resins. These materials form strong bonds. The paper keeps its shape even when wet. You can use it for tough jobs. The strength does not fade when you add water.
Can you use wet strength tissue paper for food?
Yes, you can use it for food. The paper keeps its strength when wet. It does not break or tear. You see it in food wraps and liners. Always check if the product is safe for direct food contact.
Why does wet strength matter in art projects?
You need strength for art that uses glue or paint. Wet strength tissue paper lets you layer, fold, or color without tearing. The paper holds up when wet. Your projects stay bright and strong. You get better results every time.
How do you test the strength of tissue paper when wet?
You can dip a strip in water and pull gently. If the paper keeps its strength, it will not break. You can also stretch it or press on it. Wet strength tissue paper stays together. You see the difference right away.
Is wet strength tissue paper eco-friendly?
Many brands now use eco-friendly resins and fibers. You get strength and wet resistance without harming the planet. Look for recycled content or certifications. The paper keeps its strength when wet and breaks down safely after use.
Tip: Always choose products that balance strength, wet durability, and environmental care.



























