
Thermal paper is everywhere—at checkout counters, ticket booths, and shipping stations. But have you ever wondered why so many industries rely on it instead of regular paper? The benefits of using thermal paper go beyond just printing without ink.
In this post, you’ll learn what thermal paper is, how it works, and why it’s become a go-to solution for fast, cost-effective, and high-quality printing. From POS systems to barcode labels, we’ll explore its practical advantages and help you understand if it’s right for your business.
What Makes Thermal Paper Unique?
What is thermal paper made of?
Thermal paper may look like regular paper, but it’s layered with special materials that make it react to heat. These layers are what allow images and text to appear without using ink or toner. Each component has a role that helps with fast, sharp, and clean printing.
Base Paper
This is the foundation of thermal paper. It's made from wood pulp and acts as the structure that supports all other layers. While it feels smooth, it’s built to handle high heat without warping or curling during the printing process.
Thermal Coating
This layer is the real workhorse. It contains colorless dye and an acid-based developer. When heated, these chemicals react, turning dark and forming readable prints. It’s very thin but powerful.
Optional Topcoat or Precoat Layers
Some thermal papers have an extra coating. The precoat improves smoothness and heat sensitivity. The topcoat protects the print surface from moisture, oils, or light—helpful in busy or harsh settings like kitchens or hospitals.
Key Layers in Thermal Paper:
| Layer Type | Function |
| Base Paper | Provides structure and thickness |
| Thermal Coat | Produces image when heated |
| Precoat Layer | Improves heat response and smoothness |
| Topcoat Layer | Adds protection against external elements |
How does thermal printing work?
Thermal printing doesn’t spray ink or press against ribbons. Instead, it uses controlled heat to trigger chemical changes on the paper. The result? Quick, quiet, and clean prints every time.
Direct Thermal Printing vs. Thermal Transfer Printing
Direct Thermal Printing
The printhead touches the paper directly. Heat activates the thermal layer and creates text or images. It’s fast and quiet, but not the best for long-term storage.
Thermal Transfer Printing
Here, heat melts ink from a ribbon onto the paper. The result is sharper, more durable prints. It’s ideal for labels that need to survive wear or handling.
Heat-Sensitive Chemical Reactions
Inside the thermal coating, chemicals lie dormant until heated. When the printhead gets hot, it melts dye crystals and mixes them with a developer. This makes the image visible. The process is precise—only the heated spots react.
Quick Look: Thermal Printing Methods
| Method | Uses Heat? | Needs Ribbon? | Best For |
| Direct Thermal Printing | Yes | No | Receipts, short-term labels |
| Thermal Transfer | Yes | Yes | Shipping, inventory, archiving |

Thermal Paper 2 1 4 Paper Rolls
Advantages of Using Thermal Paper
1. Faster Printing Speeds
Thermal printers produce images in milliseconds. The paper reacts instantly to heat, so there’s no drying time. This makes it perfect for fast-paced places like retail counters or busy restaurants where speed really matters.
No ink drying time, prints appear the moment heat is applied.
Reduces line wait times during peak hours.
Supports multiple transactions per minute without delays.
2. No Ink, No Toner Needed
Thermal printing skips ink entirely. The paper does the work—heat creates the image. That means fewer things to replace, fewer interruptions, and cleaner prints overall.
No need for ink cartridges or toner refills.
No mess from leaking cartridges or smudged ink.
Only one supply to stock: thermal paper rolls.
3. Low Maintenance Requirements
Thermal printers have fewer moving parts than standard printers. Because there’s no ink to clog or ribbons to tangle, they rarely break down. Less maintenance means more uptime.
| Feature | Thermal Printers | Ink/Toner Printers |
| Ink or Toner Needed | No | Yes |
| Moving Parts | Very few | Many |
| Cleaning Frequency | Occasionally | Frequently |
| Jam Likelihood | Low | Moderate to High |
4. High Print Quality
Text and images printed on thermal paper are sharp and easy to read. It’s especially useful for barcodes and labels, where clarity is key. Even small fonts print cleanly.
Produces precise lines, clean graphics, and bold text.
Great for printing scannable barcodes and QR codes.
No ink spreading, so text stays sharp.
5. Longer Print Lifespan (Under Proper Conditions)
When stored away from heat and sunlight, thermal paper prints can last for years. They won’t smudge or smear like ink-based prints if handled properly.
Resistant to moisture, fingerprints, and rubbing.
Safe to use for temporary records or archive copies.
Proper storage keeps documents readable over time.
6. Cost Savings Over Time
Buying ink or toner regularly adds up. Thermal paper eliminates that cost. Even better, thermal printers need less repair work, saving more in the long run.
Fewer supplies means fewer expenses over time.
Less downtime equals more productivity.
Bulk paper rolls are more affordable than refills.
7. Compact and Storage-Friendly
Thermal paper rolls are small and lightweight. They fit easily into drawers or storage boxes. For mobile devices and compact printers, they’re an ideal match.
Easier to restock and carry than bulkier paper stacks.
Saves space in tight workspaces or storage rooms.
Allows longer printing before needing replacement.
8. Versatile Across Industries
Thermal paper is used just about everywhere—from grocery stores to labs. Because it works with many types of thermal printers, one solution fits a range of needs.
Useful in retail, healthcare, logistics, banking, and ticketing.
Compatible with mobile, desktop, and industrial printers.
Suitable for receipts, labels, tags, and reports.
Where is Thermal Paper Commonly Used?
Retail and Point of Sale (POS)
Every time we buy something at a store, there’s a good chance the receipt is printed on thermal paper. POS systems rely on fast, reliable printing to keep lines moving, and thermal paper fits that role perfectly.
Used in grocery stores, boutiques, cafes, and gas stations.
Prints receipts, transaction summaries, and customer bills.
Reduces wait times with instant printouts at checkout.
| Retail Use Case | Purpose |
| Receipts | Customer purchase records |
| Credit card slips | Payment confirmations |
| Gift receipts | Return and exchange proof |
Shipping and Logistics
Thermal paper is ideal for shipping environments. Warehouses and logistics teams need labels that print quickly and stick well. Thermal labels handle all that—plus barcodes scan cleanly.
Used for box labeling, order tracking, and barcode scanning.
Labels remain readable even during rough transport handling.
Saves time when printing in bulk for outgoing packages.
Common Thermal Paper Uses in Shipping:
Shipping labels for carriers like FedEx, UPS, DHL
Barcode tags for inventory systems
Sorting slips for warehouse shelves
Healthcare and Laboratory Environments
In hospitals and labs, accurate records are critical. Thermal paper helps track patients and samples without messy ink. It supports fast, smudge-free label creation for sensitive materials.
Prints patient wristbands, test tube labels, prescription tags.
Works with handheld thermal printers for on-the-go tasks.
Resistant to minor moisture exposure found in lab settings.
| Application | Use |
| Specimen containers | Labeling for blood, tissue, samples |
| Patient ID wristbands | Real-time tracking in clinics |
| Medication labels | Quick printouts for dosage instructions |
Transportation and Ticketing
Thermal paper is often used where speed and readability are key. Think bus tickets, boarding passes, parking slips—it’s used anywhere time-stamped printing is needed.
Airports, subways, and events rely on thermal tickets.
Eliminates delays in issuing boarding passes or fare receipts.
Tickets hold up during short-term handling and travel.
Examples in Transit and Events:
Airline boarding passes with barcode
Automated parking receipts from kiosks
Event entry passes for concerts or sports
Types of Thermal Paper
Direct Thermal Paper
Direct thermal paper is designed for short-term use, often seen in receipts and tickets. It relies on heat-sensitive coating to produce images, making it quick and efficient. However, it has a major drawback: exposure to heat, light, or friction can cause the print to fade quickly. This makes it ideal for applications where longevity isn’t a primary concern.
Thermal Transfer Paper
Thermal transfer paper uses a ribbon to transfer ink onto the surface, producing more permanent prints. The print is more resistant to fading, making this type of paper perfect for durable labeling applications, such as barcodes or shipping labels. It’s commonly used in warehouses or manufacturing settings where the print needs to last longer.
Top-Coated Thermal Paper
Top-coated thermal paper has a protective layer that shields it from moisture, oils, and friction. This coating makes the paper more durable, ensuring that prints stay intact even in tough environments. It's frequently used in the food industry for labeling, where exposure to moisture is a concern. It also works well for high-traffic environments where wear and tear are common.
Carbonless and Multi-layered Thermal Options
Carbonless and multi-layered thermal papers are essential when multiple copies of a document are needed. These papers are used in multipart forms, such as invoices, contracts, and shipping documents, ensuring that a duplicate is created without the need for carbon paper. Their ability to handle multiple layers makes them ideal for use in office or business settings where documentation is key.
How to Choose the Right Thermal Paper
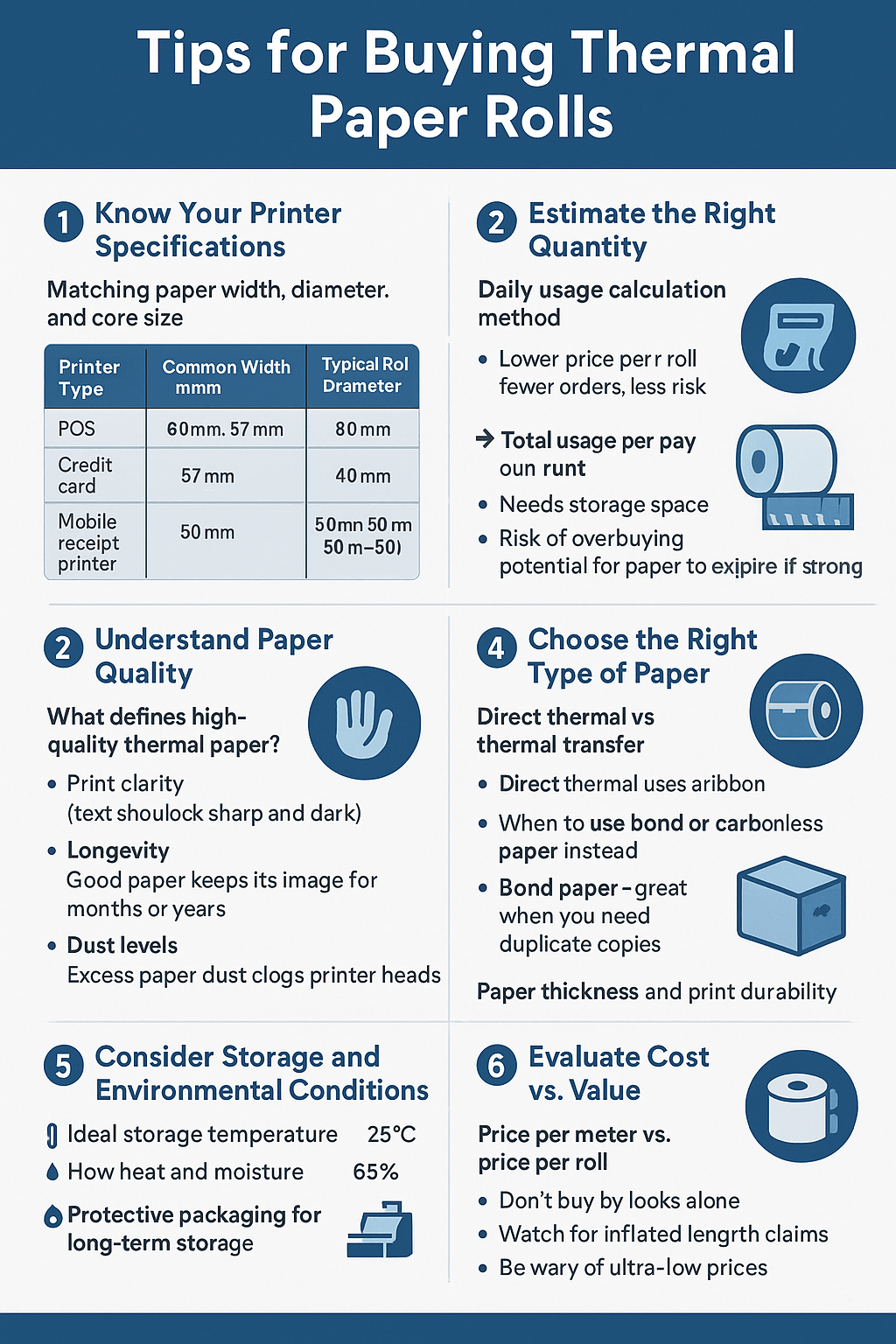
Factors to Consider
Printer Compatibility: Make sure the paper’s width, core size, and length match your printer’s requirements to avoid issues during printing.
Print Durability Needs: If your prints need to last longer, choose thermal paper designed to resist fading from heat, light, or friction.
Surface Smoothness and Coating: A smooth surface ensures even printing, while the coating affects the print’s longevity. Pick one based on your specific needs.
Testing Thermal Paper Quality
Testing thermal paper quality can help you make an informed decision. The heat reaction test shows how well the paper reacts to heat and if it produces clear prints. You can also evaluate the appearance and texture to ensure it meets your standards. Look for a smooth surface and even coating, which contributes to better print performance and longer-lasting results.
Thermal Paper vs. Traditional Paper Printing
Key Comparison Points
Speed: Thermal printing is faster than traditional methods because it doesn’t require ink or toner. The printing process is nearly instant, making it ideal for high-volume settings like point-of-sale terminals or ticket printing.
Maintenance: Thermal printers require less maintenance than traditional ink-based printers. There are no ink cartridges to replace, which reduces the need for regular servicing and keeps things simple.
Cost per Print: While thermal paper may seem more expensive upfront, it often ends up being cheaper per print due to the elimination of ink costs. However, the overall cost depends on paper quality and print volume.
Suitability by Industry: Thermal paper is perfect for industries like retail, hospitality, and transportation, where speed and convenience are essential. Traditional paper printing, however, remains essential for more complex or long-lasting documentation, like books or reports.
Common Concerns with Thermal Paper
Will thermal prints fade over time?
Yes, thermal prints can fade, especially when exposed to heat, light, or friction. Conditions like high temperatures or sunlight can accelerate the fading process, making prints less readable. Proper storage in cool, dry places can help preserve the print quality for a longer period. If longevity is crucial, it's important to consider paper with added protection or coating.
Is thermal paper safe for all uses?
Handling and Storage Tips: Thermal paper should be handled with care to avoid heat exposure and direct light. Store it in a cool, dry environment, away from direct sunlight and high temperatures, which can cause fading or damage.
Common Industry Practices: In industries like retail or transportation, thermal paper is used for quick, temporary prints like receipts or tickets. These are typically not meant to last long. For long-term documentation, industries often opt for more durable materials, such as carbonless or archival paper.
Conclusion
Thermal paper offers numerous advantages, including faster printing speeds, lower maintenance costs, and high-quality prints. Its versatility across industries and reduced need for consumables make it a smart choice for businesses looking to streamline operations. With proper care, thermal paper provides reliable, cost-effective solutions for various uses.
Choosing the right thermal paper depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like print durability and compatibility with your printer. By selecting the appropriate type and ensuring proper storage, you can maximize the benefits and performance of thermal paper for your business or organization.
FAQs
How long do thermal prints last?
Thermal prints can last from a few days to a few months, depending on storage conditions and exposure to heat.
Can thermal paper be used in any printer?
No, thermal paper is only compatible with thermal printers, not standard inkjet or laser printers.
Why is thermal paper cheaper in the long run?
Thermal paper eliminates ink and toner costs, making it more affordable over time despite higher initial paper costs.
What sizes do thermal paper rolls come in?
Thermal paper rolls come in various sizes, including 2”, 3”, and 4”, depending on printer specifications and industry needs.
Reference Sources
[1] https://pandapaperroll.com/5-benefits-using-thermal-paper-rolls/
[2] https://www.szxdpospaper.com/news/170-thermal-paper-rolls-and-their-advantages-over-ordinary-paper.asp
[3] https://graphictickets.com/the-significance-of-thermal-paper-in-the-restaurant-industry/
[4] https://www.goldenpapergroup.com/advantages-and-guide-to-using-colored-thermal-paper.html
[5] https://ponypackaging.com/blogs/news/the-top-10-benefits-of-using-thermal-paper-1
[6] https://telemarkcorp.com/learn-the-top-advantages-of-thermal-receipt-paper/



























